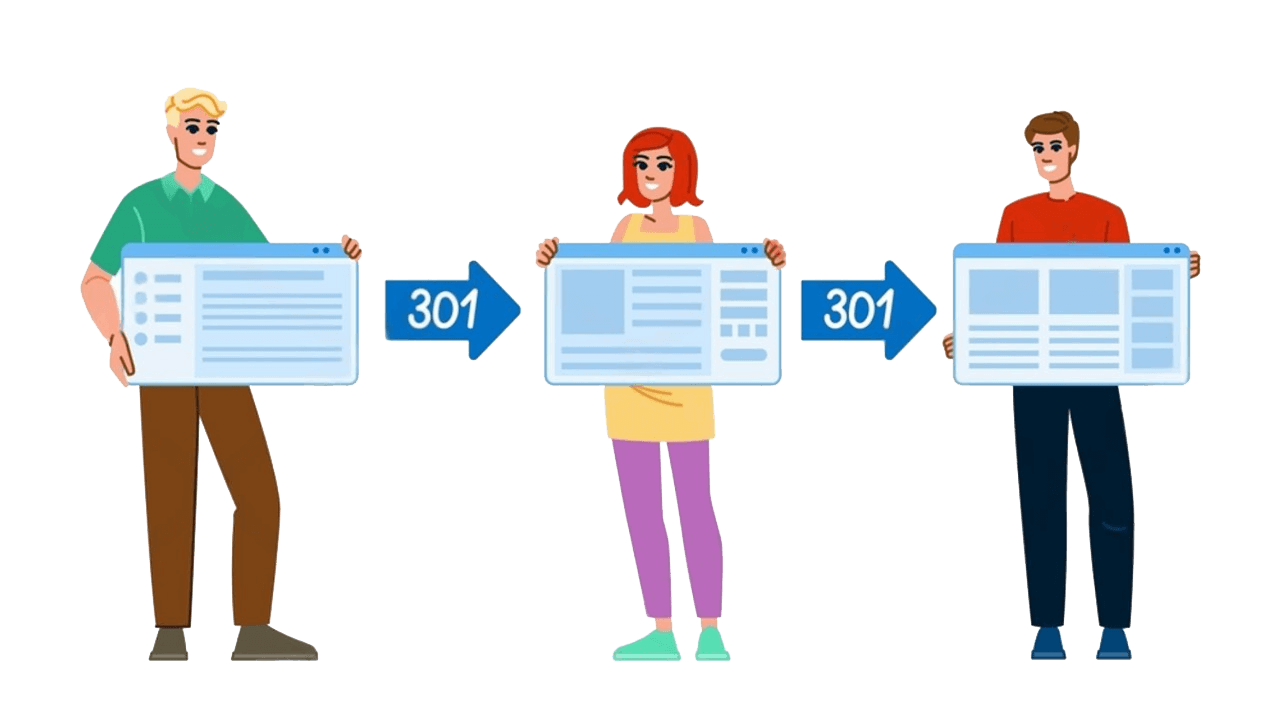
A redirect chain, also known as multiple redirects or cascading redirections, occurs when a URL redirects to another URL, which then redirects to yet another, creating a sequence of consecutive redirects before reaching the final destination.
Instead of a direct redirection from one URL to another, the request passes through multiple intermediary URLs, increasing page load time and affecting search engine crawling, user experience, and SEO rankings.
Unlike a standard redirect, where a URL forwards traffic directly to the final destination, a redirect chain introduces multiple hops.
While a single 301 redirect retains SEO value and ensures a seamless transition, chained redirects weaken link equity, slow down page load speed, and risk exceeding browser redirection limits.
Search engines like Google may stop following excessive redirects, leading to indexing issues and lost rankings.
URL Redirect chains commonly occur due to outdated redirection rules, improper website migrations, or cumulative redirections over time.
They create inefficiencies in server response handling, URL forwarding, and crawl budget allocation, making it essential to detect and fix them promptly.
How Redirect Chains Work?
When a browser or search engine requests a URL, the server responds with an HTTP status code indicating whether the requested page has moved.
If a redirect exists, the browser follows the redirection path until it reaches the final URL. A redirect chain occurs when multiple redirects are involved in this process.
Example of a Redirect Chain:
- User requests
https://example.com/old-page - The server responds with 301 Moved Permanently → Redirects to
https://example.com/intermediate-page https://example.com/intermediate-pageresponds with another 301 redirects → Redirects tohttps://example.com/new-page- The browser finally lands on
https://example.com/new-page
This multi-step URL forwarding can slow down page load times and negatively impact search engine crawlers, leading to crawl inefficiencies.
What Happens in a Redirect Chain?
A redirect chain forces a browser or search engine to make multiple requests before reaching the final URL, resulting in:
- Increased Load Time: Each additional redirect increases the time it takes for the page to load.
- Wasted Crawl Budget: Search engines like Google allocate a crawl budget for each website, and excessive redirects can waste resources.
- Loss of Link Equity: SEO value (PageRank) weakens with every additional redirect in the sequence.
- Higher Risk of Redirect Loops: If misconfigured, a chain can turn into an infinite redirect loop, causing an error.
Is a Redirect Chain Bad for SEO?
Yes, redirect chains can harm SEO by slowing indexing, reducing link equity, and creating a poor user experience.
Effects of Multiple Redirects on SEO:
| Issue | SEO Impact |
|---|---|
| Slow Page Load Time | Longer redirects delay page rendering. |
| Loss of Link Equity | Each redirect weakens the SEO value passed. |
| Crawl Inefficiency | Googlebot may stop following too many redirects. |
| Increased Bounce Rate | Users may leave before reaching the final page. |
To maintain search rankings and crawl efficiency, websites should minimize redirect chains and ensure that redirections lead directly to the final URL.
How to Detect Redirect Chains?
Use browser tools, command-line utilities, or online redirect chain checker tools to check 301 redirect chains.
1. Checking Redirect Chains in Chrome Developer Tools
- Open Google Chrome.
- Press
F12orCtrl + Shift + I(Windows) /Cmd + Option + I(Mac) to open Developer Tools. - Click on the Network tab and enable Preserve Log.
- Enter the URL and refresh the page (
F5). - Find the request in the Name column and check the Response Headers.
- Look at the
Locationfield to see if multiple redirections occur.
2. Using an Online Redirect Chain Checker
For bulk testing and analysis of redirect chains, use Optimizo.io Bulk Redirect Checker to:
- Identify multiple redirects in one request.
- Detect chained link redirection issues.
- Ensure 301 and 302 redirects are correctly implemented.
3. Checking Redirect Chains via cURL
For a command-line approach, use cURL to track redirections:
curl -IL https://example.com/old-pageEach HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently response indicates a redirection step. A redirect chain is present if multiple appear before reaching the final destination.
Redirect Chain vs Redirect Loop
A redirect chain involves multiple consecutive redirects before reaching the final page. A redirect loop occurs when URL A redirects to URL B, which redirects back to A, causing an infinite loop.
How to Break a Redirect Chain
To optimize a website, follow the best practices for managing redirects:
- Use direct 301 redirects to avoid unnecessary steps.
- Check redirects regularly using redirect tracking tools.
- Limit redirect chains to a maximum of two hops to retain link equity.
- Ensure HTTPS redirection is direct to prevent mixed-content errors.
Best Practices for Managing Redirect Chains
To optimize redirect performance and SEO impact, follow these guidelines:
✅ Use 301 redirects instead of 302 for permanent URL changes.
✅ Limit chains to a maximum of two redirects to maintain page speed.
✅ Monitor redirect chains regularly using Optimizo.io Bulk Redirect Checker.
✅ Avoid linking to redirected URLs—update internal links to point directly to the final destination.
✅ Ensure consistency between HTTP and HTTPS redirections to prevent unnecessary chains.
How to Track Multiple Redirects
To continuously monitor and test redirect paths, use:
- Google Search Console → Reports on redirect errors.
- Optimizo.io Redirect Chain Checker → Bulk analysis of chained URLs.
- Screaming Frog SEO Spider → Detects multiple redirects during website audits.
Regular tracking helps prevent redirect loops, slow page loads, and loss of SEO value.

Hamza Sarfraz is an experienced SEO and digital marketing strategist with over six years of expertise in boosting online visibility and growth. Working as a Digital Marketing Manager at MARKETERS.PK focuses on developing data-driven SEO strategies, planning projects effectively, and optimizing performance marketing to help businesses scale.
With a strong interest in technology, SEO, and digital marketing, Hamza shares practical insights to help businesses and professionals keep updated. His hands-on approach to organic search, content marketing, and conversion optimization helps brands strengthen their presence and increase revenue.