A redirect loop, also known as an infinite redirect cycle or looping URL redirects, occurs when a URL continuously redirects to another URL in a circular pattern, preventing the page from loading.
This causes browsers to repeatedly follow redirections without reaching the final destination, leading to a “Too Many Redirects” error message.
What Does Redirect Loop Mean
Redirect loops differ from regular URL redirects or redirect chains in that they create an endless cycle, trapping users and search engine crawlers in an unresolved sequence of redirections.
Unlike a 301 redirect that moves a URL permanently or a 302 redirect that temporarily forwards traffic, a redirect loop never resolves to a valid page, resulting in website inaccessibility and SEO issues.
Common causes of redirect loops include misconfigured .htaccess rules, conflicting redirect settings, server misconfigurations, or improper CMS/plugin redirects.
When a website gets stuck in a continuous URL loop, it can disrupt user access, negatively affect SEO rankings, and waste server resources.
Why Does a Redirect Loop Happen?
A redirect loop occurs when redirection rules create an unresolved cycle between URLs. This usually happens due to misconfigured settings, where one page redirects to another that eventually redirects back to the original page.

Common Causes of Redirect Loops:
- Conflicting Redirect Rules in .htaccess (Apache Servers) – A wrongly configured 301 or 302 redirect in the
.htaccessfile can lead to an endless redirection loop. - Misconfigured Nginx Redirect Rules – Incorrect server-side redirection in the
nginx.conffile can cause looping URL redirects. - Incorrect HTTP to HTTPS Redirects – When both HTTP and HTTPS are set to redirect to each other, a self-referencing redirection occurs.
- CMS Plugin Conflicts (WordPress, Shopify, Joomla, Drupal, etc.) – Multiple redirect settings from different plugins can create cyclic redirects.
- Incorrect Canonical Tags or Meta Refresh Redirects – If a page’s canonical URL points to itself incorrectly, it can cause an infinite 301 redirect.
- Server Misconfiguration or Proxy Issues – Web server settings (e.g., Cloudflare misconfigurations) can result in a non-stop redirect chain.
How to Check for Redirect Loops
Detecting a redirect loop is crucial to restoring website accessibility and fixing SEO issues. Several methods can be used to check infinite redirect cycles and diagnose errors.
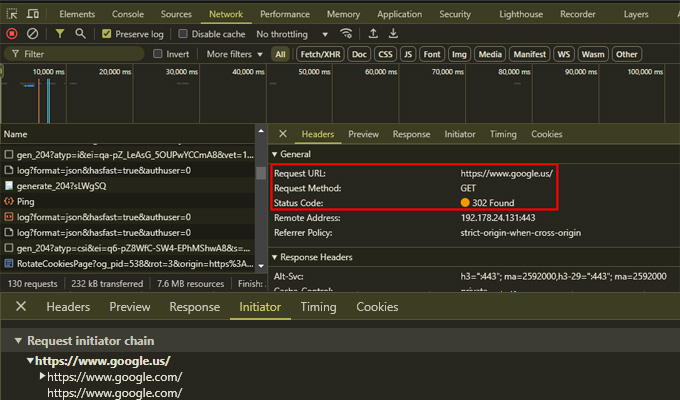
1. Checking for Redirect Loops in Browser Developer Tools
- Open your browser e.g. Google Chrome.
- Press
F12orCtrl + Shift + I(Windows) /Cmd + Option + I(Mac) to open Developer Tools. - Click on the Network tab and enable Preserve Log.
- Enter the problematic URL and refresh the page.
- Look for repeated requests to the same URLs under the Name column.
- Check the Response Headers for recurring
301or302status codes.
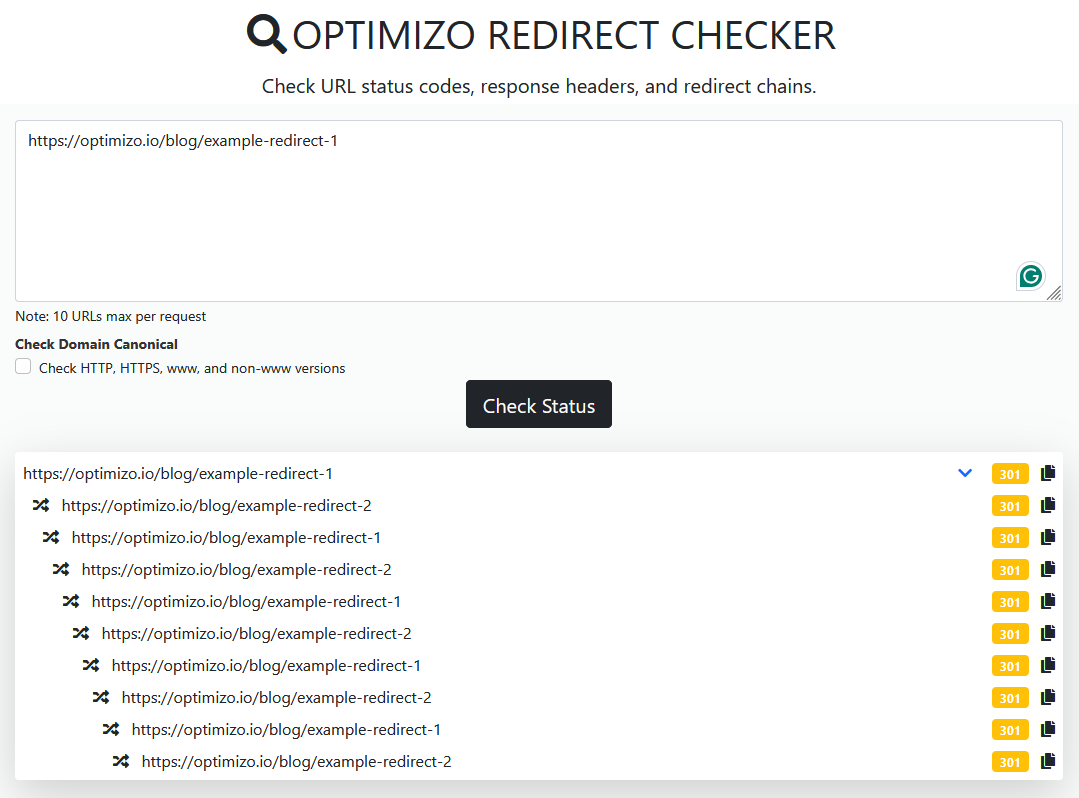
2. Using an Online Redirect Loop Checker
For an automated redirect tracking tool, use Optimizo.io Bulk Redirect Checker to:
- Detect repeating redirect patterns and cyclic URL forwarding.
- Check if a site is stuck in an infinite 301 redirect.
- Identify browser error messages related to excessive redirects.
3. Diagnosing Redirect Loops with Curl Command
For advanced users, the cURL command helps track redirections at the server level:
curl -IL https://example.comIf the output shows the same URL repeatedly redirecting with 301 Moved Permanently or 302 Found, a redirect loop is present.
Redirect Loop vs Redirect Chain
A redirect loop is different from a redirect chain.
| Redirect Chain | Redirect Loop |
|---|---|
| Multiple redirects before reaching the final page. | An endless cycle that prevents access to the final page. |
| May affect SEO but does not break functionality. | Causes ERR_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS and prevents page loading. |
| Slows down page speed but does not create an infinite cycle. | Traps users and search engines in an unresolved loop. |
Best Practices for Preventing Redirect Loops
✅ Use direct redirects – Avoid multiple intermediary steps.
✅ Check redirect rules regularly – Audit .htaccess, nginx.conf, and CMS settings.
✅ Avoid HTTPS to HTTP redirects – Ensure consistent SSL enforcement.
✅ Test redirects before deployment – Use Optimizo.io Redirect Checker to detect misconfigurations.
✅ Limit plugin-based redirections – Manage redirects at the server level for better control.
A redirect loop occurs when a URL is caught in an infinite redirect cycle, leading to browser errors, SEO issues, and site inaccessibility.
Misconfigured .htaccess rules, conflicting CMS plugins, or incorrect server settings are common causes of this issue. Fixing redirect loops involves analyzing server response headers, testing redirect paths, and correcting misconfigured rules.
Using tools like Optimizo.io Bulk Redirect Checker ensures efficient redirect tracking and troubleshooting, preventing looping URL redirects and improving website performance.

Hamza Sarfraz is an experienced SEO and digital marketing strategist with over six years of expertise in boosting online visibility and growth. Working as a Digital Marketing Manager at MARKETERS.PK focuses on developing data-driven SEO strategies, planning projects effectively, and optimizing performance marketing to help businesses scale.
With a strong interest in technology, SEO, and digital marketing, Hamza shares practical insights to help businesses and professionals keep updated. His hands-on approach to organic search, content marketing, and conversion optimization helps brands strengthen their presence and increase revenue.