A redirect chain happens when one URL redirects to another, which then redirects to another, forming a sequence of multiple redirects before reaching the final destination. This process slows down website performance and affects search rankings. A redirect loop occurs when a URL redirects back to itself or creates an endless cycle of redirections between multiple pages. This prevents access to the website and causes browser errors such as “ERR_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS”.
Simplest Way to Fix Redirect Chains & Loops
Identify the problematic redirects within your website’s configuration to fix redirect chains and loops. Then, directly point the initial URL to the final destination using a single 301 redirect, effectively removing any unnecessary intermediary redirects that create the chain or loop. This can usually be done by reviewing your server configuration files, CMS settings, or relevant plugins, depending on your platform.
Key steps to fix redirect chains and loops:
- Identify the issue: Use browser developer tools: Access your browser’s developer tools to see the HTTP status codes of redirects and identify where the chain or loop is occurring.
- Check website analytics: Look for patterns in user behavior that might indicate redirect issues, such as high bounce rates on specific pages.
- Use website auditing tools: Utilize dedicated SEO tools to scan your website for redirect chains and loops.
Analyze the redirect chain/loop:
- Trace the redirect path: Follow the sequence of redirects from the initial URL to understand where the loop is created.
- Check redirect types: Ensure all redirects are using the proper HTTP status code, ideally 301 (permanent redirect).
Fix the redirect issue:
- Directly redirect to the final destination: Modify the redirect configuration to point the initial URL directly to the intended final page, eliminating unnecessary intermediary redirects.
- Review server configuration files: Depending on your web server (Apache, Nginx), access the relevant configuration files to adjust redirects.
- Check CMS settings: If using a content management system like WordPress, review plugin settings and relevant redirect options within the CMS interface
For advanced methods, refer to the techniques outlined below ⬇️.
Look for Existing Redirects (Chains & Loops) and Correct Them
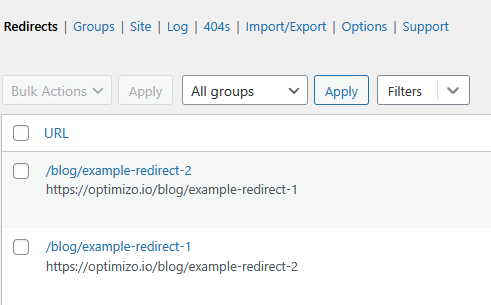
One of the most common reasons for redirect loops is incorrect redirection rules. You may have set up a redirect that sends a URL to another page that eventually redirects back to the original URL.
Steps to Identify and Fix Incorrect Redirects:
- Check the redirects you have created in your CMS, server configuration, or redirection plugin.
- List all active redirects and find any that point back to a URL that is already redirected.
- Delete unnecessary redirects or modify them to point directly to the final URL.
- Ensure all URLs redirect in a single step instead of creating a looping pattern.
Example of a Faulty Redirect Causing a Loop:
old-page → new-page-1 → old-page(Creates an infinite cycle)
Fixed Redirect:
old-page → new-page-1(Direct path, avoids looping)

How to Fix Redirect Chains?
The best way to resolve a redirect chain is to remove unnecessary redirects and point old URLs directly to the final destination.
Fixing Redirect Chains in .htaccess (Apache Servers)
If redirect chains are caused by incorrect .htaccess rules, update them by ensuring a direct path to the final URL:
Before (Incorrect – Causes a Chain):
Redirect 301 /old-page https://example.com/intermediate-page
Redirect 301 /intermediate-page https://example.com/new-pageAfter (Correct – Direct Redirection):
Redirect 301 /old-page https://example.com/new-pageFixing Redirect Chains in Nginx
If using Nginx, modify the redirect rule to remove intermediary steps:
Before (Chain Exists):
rewrite ^/old-page$ https://example.com/intermediate-page redirect;
rewrite ^/intermediate-page$ https://example.com/new-page redirect;After (Fixed – Direct Redirect):
rewrite ^/old-page$ https://example.com/new-page redirect;Removing Redirect Chains in WordPress / Joomla / Magento / Shopify & Others
For WordPress sites, check for excessive redirects caused by plugins:
- Go to Settings → Permalinks and reset permalinks.
- Use Redirection Plugin to check if any sequential URL redirections exist.
- Manually update redirection rules, ensuring they point directly to the final URL.
How to Fix Redirect Loops?
Fixing a redirect loop requires checking and correcting incorrect redirection settings. One of the most common reasons for redirect loops is incorrect redirection rules. You may have set up a redirect that sends a URL to another page that eventually redirects back to the original URL.
Steps to Identify and Fix Incorrect Redirects:
- Check the redirects you have created in your CMS, server configuration, or redirection plugin.
- List all active redirects and find any that point back to a URL that is already redirected.
- Delete unnecessary redirects or modify them to point directly to the final URL.
- Ensure all URLs redirect working in a single step instead of creating a looping pattern.
Example of a Faulty Redirect Causing a Loop:
old-page → new-page-1 → old-page(Creates an infinite cycle)
Fixed Redirect:
old-page → new-page-1(Direct path, avoids looping)
Check .htaccess File (For Apache Servers)
If your site runs on Apache, incorrect rules in the .htaccess file may be causing a loop.
- Access the
.htaccessfile via FTP or cPanel File Manager. - Look for conflicting redirects.
Example of a Bad Redirect Rule (Causing a Loop)
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://example.com/$1 [R=301,L]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://example.com/$1 [R=301,L]The second rule forces an HTTP to HTTPS loop. Remove or fix the incorrect rule.
Corrected Redirect Rule
RewriteEngine On
RewriteCond %{HTTPS} off
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ https://example.com/$1 [R=301,L]Fix Nginx Redirect Configuration
If using Nginx, incorrect redirect settings can cause loops.
- Open the
nginx.conffile and check for faulty redirects.
Incorrect Rule (Causing a Loop)
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}
server {
listen 443 ssl;
server_name example.com;
return 301 http://example.com$request_uri;
}The second rule redirects HTTPS back to HTTP, creating a loop.
Corrected Rule
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com;
return 301 https://example.com$request_uri;
}For WordPress/CMS Users
Common WordPress redirect loop errors include:
- ERR_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS error in Browser
- WordPress plugin redirect loop
- Infinite redirect cycle caused by SSL settings
Steps to Fix a Redirect Loop in WordPress:
- Disable Conflicting Plugins:
- Access wp-admin and go to Plugins → Installed Plugins.
- Deactivate any redirection or security plugins.
- Check WordPress Site URL Settings:
- Go to Settings → General.
- Ensure WordPress Address (URL) and Site Address (URL) are correct (e.g.,
https://example.com).
- Reset .htaccess Rules:
- Edit the
.htaccessfile in the root directory. - Replace the existing rules with:
-
# BEGIN WordPress RewriteEngine On RewriteBase / RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L] RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-f RewriteCond %{REQUEST_FILENAME} !-d RewriteRule . /index.php [L] # END WordPress
- Edit the
How to Fix “ERR_TOO_MANY_REDIRECTS” Error
This browser error occurs when a website has excessive redirects. 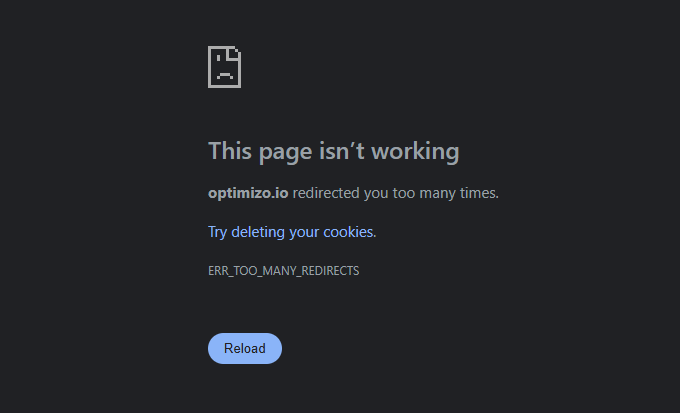
- Open browser settings and clear cookies.
- Restart the browser and check the website.
Disable Plugins and Themes in WordPress
- If unable to access the dashboard, rename the
/wp-content/plugins/folder via FTP. - Check Settings → General and ensure “WordPress Address” and “Site Address” match.
Check and Fix .htaccess Rules
- Open
.htaccessand remove duplicate or incorrect redirects. - Reset
.htaccessby replacing it with:# BEGIN WordPress RewriteEngine On RewriteBase / RewriteRule ^index\.php$ - [L]
Ensure No HTTPS and HTTP Conflicts
- Websites running on HTTPS must have a single redirect rule.
- Remove any conflicting HTTP-to-HTTPS redirects in
.htaccessornginx.conf.
Test and Verify Fixes
- Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection Tool to confirm correct redirects.
- Manually visit the affected URLs in a browser to ensure they redirect correctly.
- Run another site crawl using Screaming Frog to confirm that redirect loops or chains are eliminated.
- Use a redirect checker to verify your URL redirections.
Following these steps, you can correct misconfigured redirects and ensure your website’s redirection structure remains efficient, improving user experience and SEO.

Hamza Sarfraz is an experienced SEO and digital marketing strategist with over six years of expertise in boosting online visibility and growth. Working as a Digital Marketing Manager at MARKETERS.PK focuses on developing data-driven SEO strategies, planning projects effectively, and optimizing performance marketing to help businesses scale.
With a strong interest in technology, SEO, and digital marketing, Hamza shares practical insights to help businesses and professionals keep updated. His hands-on approach to organic search, content marketing, and conversion optimization helps brands strengthen their presence and increase revenue.