Broken links are links on a website that don’t work because the page they lead to has been removed moved, or the URL is incorrect. When visitors click on these links, they see an error instead of the expected content, which can be frustrating and make your website seem unreliable. Fixing broken links is important because they can damage your website’s search engine rankings and annoy your visitors. Using Optimizo URL Status Checker, you can easily find and fix broken links to keep your website running smoothly and ensure a better user experience.
What Are Broken Links?
Broken links, also called dead links, are hyperlinks that lead to web pages that no longer exist or cannot be accessed. When someone clicks on a broken link, they typically encounter an error message, such as “404 Page Not Found,” instead of the intended content. These broken connections disrupt the flow of information and can negatively impact user experience and search engine optimization.
Types of Broken Links
- Internal Broken Links
These are links within your website that don’t work. For example, if you change a page’s URL but forget to update the internal links pointing to it, users clicking on those links will encounter an error. - External Broken Links
External broken links occur when your website links to another page that has been removed, moved, or altered without proper redirection. For instance, if you link to an article on a different website and that article is later deleted, the link will become broken. - Backlink Issues
Backlinks are links from other websites pointing to your site. If a page on your website is deleted or its URL changes without a redirect, any backlinks pointing to that page will become broken, leading visitors to an error page.
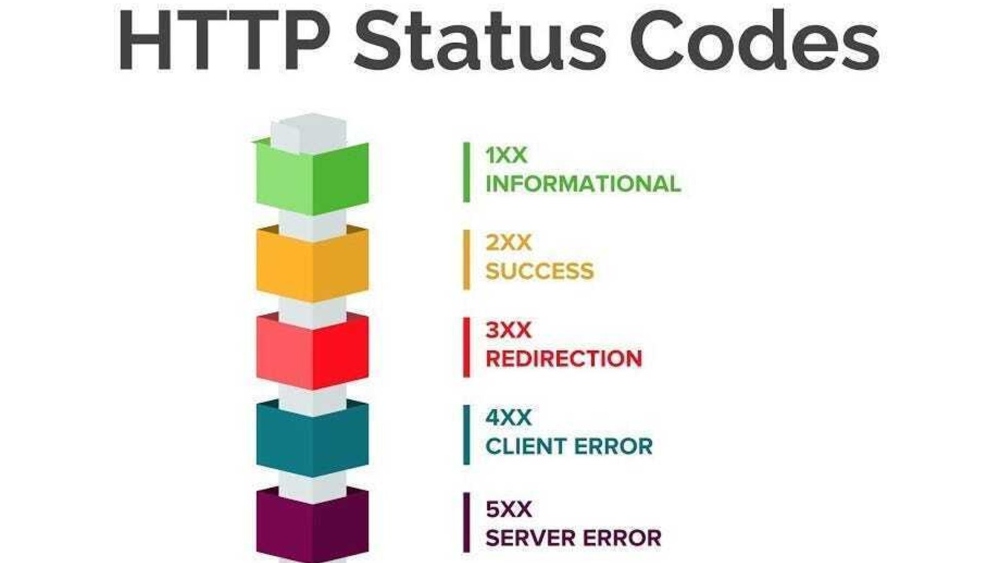
HTTP Status Code Issues
Broken links are often identified by specific HTTP status codes, which indicate the type of error. Common codes include:
- 404 (Not Found): The requested page or resource is missing or mistyped.
- 403 (Forbidden): The server refuses access, often due to permission issues.
- 500 (Internal Server Error): A server-side problem affecting the request.
- 410 (Gone): Similar to 404 but indicates intentional resource removal.
- 408 (Request Timeout): The server timed out while waiting for the request.
Some Examples of Broken Links
Here are some common real-life examples of broken links:
- Clicking on a product link in an online store and seeing a “404 Page Not Found” error because the product page was deleted.
- Visiting a blog post that links to a resource on another website, only to find the resource no longer exists.
- Landing on an error page when clicking on an outdated link shared on social media or in an email.
Why Broken Links Are a Problem
Broken links are more than just a minor inconvenience—they can significantly harm your website’s performance, reputation, and ability to retain users. Here’s how broken links impact SEO, user experience, and business outcomes.
SEO Implications
Broken links can damage your website’s search engine optimization (SEO) efforts in several ways. When search engines crawl your website, they rely on links to understand your site’s structure and content. A broken link wastes “link equity,” meaning the authority and value that link could have passed to other pages is lost. This weakens your site’s overall ranking potential.
Broken links lead to crawl errors, which search engines record as system issues. Frequent crawl errors signal that your website isn’t well-maintained, which can harm its visibility in search engine results. Over time, this can result in lower organic traffic and reduced discoverability for your content.
Additionally, if your website has too many 404 errors or broken links, Google’s crawler may reduce your crawl budget. A reduced crawl budget means fewer pages on your website will be crawled and indexed, directly impacting your indexation rate and search visibility.
User Experience
From a user’s perspective, broken links are frustrating and disruptive. When a visitor clicks on a link expecting valuable content and is instead met with an error, it creates a poor impression. This can lead to higher bounce rates as users leave your website searching for better alternatives.
Broken links also damage your website’s credibility. Visitors may perceive your site as outdated or poorly managed, which reduces their trust in your brand. This lack of trust can discourage repeat visits and long-term loyalty for websites that rely on user engagement, such as e-commerce stores or content platforms.
Business Impact
Broken links don’t just affect your SEO and user experience—they can also hurt your business outcomes. For instance, if a product link is broken, potential customers cannot complete their purchase, resulting in lost sales and revenue. Similarly, if a service page link is broken, potential clients may leave your site without learning about your offerings, leading to missed opportunities.
Broken links can drive potential customers to your competitors. Visitors who encounter errors on your website will likely look elsewhere for a more seamless experience, giving your competition an advantage.
Common Causes of Broken Links
Broken links can occur for several reasons, many of which are preventable with proper website management. Understanding these common causes can help you proactively avoid them and keep your site functional and user-friendly.
URL Structure Changes
One of the most common causes of broken links is changes to your website’s URL structure. This often happens when migrating to a new content management system (CMS) or implementing SEO-friendly URLs. If the old URLs aren’t properly redirected to the new ones, existing links within your site or from external sources will break, leading to error pages.
Misspelled URLs
A common cause of broken links is simple typographical errors in the URL. Mistakes like missing “https://” or “http://”, incorrect domain extensions, or extra spaces can result in links that do not work as intended. Even small errors in a URL can disrupt the user experience and harm your website’s functionality.
Updated URLs Without Redirects
When URLs are updated due to site restructuring, SEO improvements, or other changes, failing to set up proper redirects can lead to broken links. Links pointing to the old URLs will no longer work, creating errors for users accessing the content.
Firewall or Geolocation Restrictions
Some content may be restricted based on regional or firewall settings, which can cause links to appear broken for users in specific locations. This issue is especially common for global websites or content hosted on regionally restricted servers.
Deleted or Moved Pages
When pages are deleted or moved without setting up proper redirects, the links pointing to those pages become broken. This is particularly common during website redesigns or when outdated content is removed. Visitors and search engines encounter a dead end without a 301 redirect to guide users to a new or relevant page.
Typographical Errors in URLs
Simple URL typos, such as missing characters or incorrect domain extensions, can lead to broken links. These errors often occur when adding links manually to a website or during content updates. Even small mistakes can render a link unusable.
Expired Domains or Removed External Content
Broken links can also result from external factors, such as linking to a third-party website that no longer exists or has removed your referenced content. If the linked domain expires or the external site reorganises its content without redirects, your external links will no longer work.
Site Down or Malfunctioning Plugin Issues
Sometimes, broken links can arise because the website is temporarily down or experiencing functionality issues due to a malfunctioning plugin. These technical problems can prevent pages from loading correctly, leading to broken links and error messages. Regular site monitoring and timely plugin updates are crucial to minimise these disruptions.
How to Check for Broken Links
Identifying broken links on your website is the first step toward fixing them. You can use both manual and automated methods to find these problematic links. Here’s how you can do it effectively:
Manual Checking
Manual checking involves reviewing your website and links individually to spot broken ones. Follow these steps to check for broken links manually:
- Visit Key Pages: Open important pages on your site and test the links by clicking on them.
- Check Navigation Menus: Review your navigation menus and footer links to ensure they direct users correctly.
- Inspect Anchor Text Links: Go through your content and test the clickable links within paragraphs.
- Use Browser Extensions: Browser tools like the “Check My Links” Chrome extension can highlight broken links on a page for quick identification.
While manual checking is simple, it can be time-consuming, especially for large websites.
Automated Tools
Automated tools make checking for broken links faster and more efficient. These tools crawl your website, scanning for links that lead to errors. Here are some reliable options:
- Optimizo URL Status Checker:
The Optimizo URL Status Checker is an easy-to-use tool that quickly scans your website page for broken links and provides a detailed report of errors. It’s perfect for identifying 404 errors, redirects, and server issues, making it a go-to solution for webmasters. - Screaming Frog SEO Spider:
This powerful desktop tool crawls websites and detects broken links, duplicate content, and other issues. It’s ideal for large websites with thousands of pages. - Google Search Console:
A free tool from Google that identifies crawl errors, including broken links, across your site. - SEOptimer:
This all-in-one SEO tool includes broken link checking as part of its comprehensive website audit.
These tools save time and provide actionable insights for fixing broken links.
Monitoring Backlinks
Backlinks, or links from other websites to yours, can also break over time. Regularly monitoring these links ensures that visitors from other websites can access your content. Use the following tools to check for broken inbound links:
- Ahrefs: Tracks backlinks and notifies you when a link to your site becomes broken.
- SEMrush: Provides a backlink audit feature to detect broken inbound links.
Monitoring backlinks helps maintain your site’s credibility and SEO performance by ensuring that external links direct users to the right pages.
How to Fix Broken Links
Fixing broken links is essential in maintaining your website’s functionality, SEO performance, and user satisfaction. Below are practical methods for addressing broken links, categorized by type and situation.
Fixing Internal Links
Internal links connect one page of your website to another. Here’s how to fix them:
- Correct Typos: Typos are a common cause of broken internal links. Carefully review and correct misspelled URLs in your content, navigation menus, and footer links.
- Update Links After Moving Pages: If you’ve moved or renamed a page, ensure that all internal links pointing to the old URL are updated to reflect the new location.
Regularly checking and updating internal links ensures smooth navigation within your site and improves the user experience.
Fixing External Links
External links direct users to pages on other websites, which can break if the target content is removed or changed. Here’s how to handle broken external links:
- Find Alternative Sources: If the linked content no longer exists, search for a similar, reliable resource and update the link.
- Contact Website Owners: If the broken link points to another website, contact the site owner or administrator, requesting them to fix or redirect the link.
Maintaining functional external links preserves your content’s credibility and value to users.
Setting Up Redirects
Redirects are an effective way to handle broken links caused by URL changes or removed pages:
- 301 Redirects: Use a 301 redirect when a page has been permanently moved to a new URL. This informs search engines and users of the new location and preserves the page’s SEO value.
- 302 Redirects: Use a 302 redirect for temporarily moved pages. This ensures users are redirected while keeping the original URL intact for future use.
Implementing proper redirects prevents users from encountering error pages and helps search engines understand your site structure.
Removing Broken Links
In some cases, removing a broken link entirely is the best solution:
- When to Remove: If a broken link no longer serves a purpose and there’s no suitable replacement, it’s better to remove it to avoid confusing users.
- How to Do It Safely: Rewrite the surrounding content to ensure it remains coherent and informative after removing the link.
Removing irrelevant or outdated links keeps your website clean and professional.
Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance helps prevent broken links from becoming a recurring issue:
- Schedule Routine Audits: Use tools like the Optimizo URL Status Checker to scan your site periodically for broken links and other issues.
- Monitor Changes: Stay aware of changes to internal pages and external resources, updating links as needed.
- Educate Your Team: Train your content creators and editors on best practices for managing links, such as testing new links before publishing.
Conclusion
Fixing broken links is essential for maintaining your website’s SEO performance, user experience, and overall credibility. Broken links can frustrate visitors, harm search engine rankings, and lead to lost business opportunities. You can simplify identifying and resolving broken links by addressing these issues and using tools like Optimizo’s URL Status Checker. Take the first step toward a healthier website—use Optimizo’s URL Status Checker today to scan and fix your site effortlessly.
Gulrukh Chaudhary, an accomplished digital marketer and technology writer with a passion for exploring the frontiers of innovation. Armed with a Master’s degree in Information Technology, Gulrukh seamlessly blends her technical prowess with her creative flair, resulting in captivating insights into the world of emerging technologies.